Section: New Results
Thoracic implant
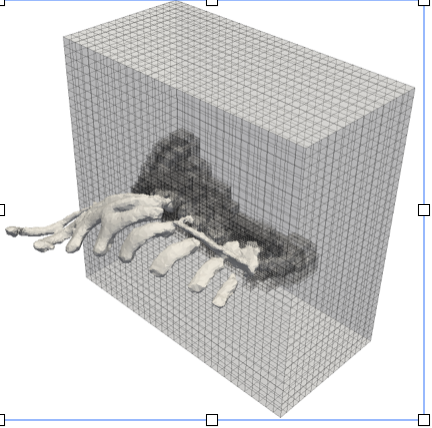
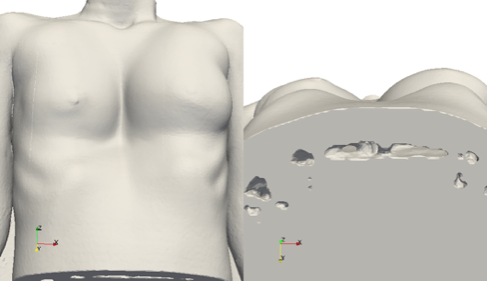
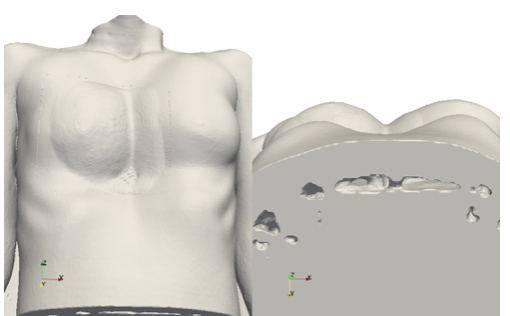
We are interested in the simulation of elastic tissus deformation in order to simulate the skin deformation due to the pose of a thoracic implant. These implants are used to fill the sternum cavity of patients affected by Pectus Excavatum syndrom. As a first step, we simulated the skin deformation with a single layer elastic model from the real bones, skin and implant geometries imported from STL files. The implant geometry has been designed on-demand by Anatomik Modeling. The single layer elastic model representing an under-skin implant, has been implemented on an octree grid to easily and automatically refine around the different geometries and keep accuracy.
|
The results obtained were qualitatively validated by Anatomik Modeling. The implant actually lays on the rib cage, under the muscles. The next step will be then to include a multi-layer elasticity model to take into account the muscles and other biological soft tissus.
Another problem linked to custom made thoracic implants is the extraction of the so-called surgical plan. It is a critical step necessary to design the implant. This plan corresponds to the surface of the rib cage. To extract it, a mass-spring model has been developed and integrated in a software prototype with a graphical interface. The resulting prototype can be used easily from on any rib cage described by a STL file.