2024Activity reportProject-TeamSYCOMORES
RNSR: 202124119E- Research center Inria Centre at the University of Lille
- In partnership with:Université de Lille, CNRS
- Team name: Symbolic analysis and Component-based design for Modular Real-Time Embedded Systems
- In collaboration with:Centre de Recherche en Informatique, Signal et Automatique de Lille
- Domain:Algorithmics, Programming, Software and Architecture
- Theme:Embedded and Real-time Systems
Keywords
Computer Science and Digital Science
- A2.1.9. Synchronous languages
- A2.3.1. Embedded systems
- A2.3.3. Real-time systems
- A2.4.1. Analysis
- A2.4.3. Proofs
- A2.6.1. Operating systems
- A7.2. Logic in Computer Science
Other Research Topics and Application Domains
- B6.6. Embedded systems
1 Team members, visitors, external collaborators
Research Scientists
- Patrick Baillot [CNRS, Senior Researcher]
- Raphaël Monat [INRIA, Researcher]
- Vlad Rusu [INRIA, Researcher]
Faculty Members
- Giuseppe Lipari [Team leader, UNIV LILLE, Professor]
- Julien Forget [UNIV LILLE, Associate Professor]
Post-Doctoral Fellow
- Leandro Moreira Gomes [UNIV LILLE]
PhD Students
- Chiara Daini [INRIA]
- Nordine Feddal [INRIA]
- Pierre Goutagny [INRIA, from Sep 2024]
- Victor Sannier [UNIV LILLE]
- Milla Valnet [LIP 6]
Interns and Apprentices
- Pierre Goutagny [ENS DE LYON, Intern, until Aug 2024]
- Romit Roy Chowdhury [INRIA, Intern, from May 2024 until Jul 2024]
Administrative Assistants
- Nathalie Bonte [INRIA]
- Karine Lewandowski [INRIA]
2 Overall objectives
The SYCOMORES project-team aims at developing a framework for the design and the analysis of embedded real-time systems based on symbolic analysis of parametric components.
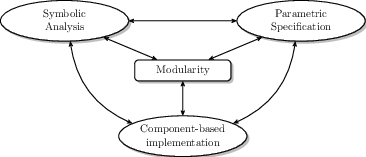
The figure show the relationship between the key terms in SYCOMORES
To reduce the complexity, we will use a modular approach to the design, development and analysis of ERTS. In particular, we will decline modularity along several directions (Figure 1):
- a component-based design and development methodology; a ERTS system is decomposed in generic, configurable and reusable components that can be combined and instantiated in the final system;
- parametric specification of inputs, configurations and properties; a component is characterised by its interface that will be specified using parameters whose concrete values are unknown at design time;
- symbolic analysis of components; by using symbolic techniques, the properties of a component will be proved correct at design time even when parameters have unknown values.
Finally, we will propose composition operators to integrate a set of components into a larger component, or into a complete system. The operators will allow to (partially or totally) instantiate parameters and connect component interfaces guaranteeing their compatibility and preserving their properties.
To this end, we will investigate several challenging problems at three different levels of abstraction, as shown in Figure 2. At the application level, we will focus on multi-rate data-flow programming languages like Scade 20, Simulink 34, or in our case Prelude35, as they are widely used in safety-critical domains like avionics and automotive. We want to tackle the notions of component, parametric interfaces and contracts in the ERTS context. We will investigate modular code generation (compilation) of a synchronous component (as opposed to a synchronous program) with real-time constraints. In the long term, we would like to prove the semantic preservation of properties of the program during compilation by using interactive proof systems.
The compiler will produce the component implementation as a set of concurrent real-time tasks with their scheduling parameters. At this level, we will work on parametric and modular worst-case execution time (WCET) analysis of tasks' code, and symbolic schedulability analysis of the components' tasks. We will also work on analysis of the correctness of system integration, and safe dynamic replacement/upgrade of components.
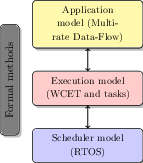
At the lowest level, we will work on the scheduler implementation in the Operating System. We will propose a hierarchical scheduling architecture, in order to provide temporal isolation to real-time components. We will formally prove the scheduler properties by using modular proof techniques in the Coq proof assistat 40, and we will provide a correct-by construction implementation of the scheduler by using code generation techniques from a Coq program specification.
As a cross-cutting activity, since safety will be a prime concern in our project, we will rely on formal methods throughout the project: synchronous programming languages, abstract interpretation, symbolic analyses and proof techniques. Our research objectives will be tightly coupled to ensure the safety of the final framework.
For instance, our tools and techniques will share proof facts (e.g. timing analysis is correct only if schedulability analysis and WCET analysis are both correct), models (e.g. the schedulability analysis, programming language and WCET analysis must share the same task model), and results (e.g. the WCET and schedulability results will impact the program design).
3 Research program
We detail the objectives by categorising them according to 3 major research axes. Within each axis, we distinguish Short Term (1-3 years) and Medium Term (2-4 years) objectives, and we describe how we will achieve them. We also detail how the objectives are related to one another. Finally, we present our Long Term (4+ years) objectives.
3.1 Axis 1: Design and implementation of RT-components
In this research axis we will focus on the programming of RT-components. We will cover programming aspects at different levels of the development process, from high-level design, to low-level implementation on distributed heterogeneous embedded platforms.
3.1.1 Short term
(A1.S1) Synchronous languages
We continue working on synchronous programming languages for generating correct-by-construction code. In particular, one of the objectives of the ANR projet CORTEVA (which was coordinated by G. Lipari, started in Jan. 2018, and lasted 48 months) was to extend the synchronous language Prelude35 to address systems with extremely variable execution time.
The language has been extended (its semantics and its compilation) with constructs to dynamically change the behaviour of a subset of the system based on rare events, like the occurrence of a large execution time of a task. The proposed extensions guarantee that the system respects correctness properties even in the presence of such rare events.
Dependencies: We rely on Parametric WCET to detect the occurence of large execution times (A2.S1).
(A1.S2) Scheduling of complex task models
Modern hardware platforms consist of heterogeneous processors with a large degree of parallelism. For example, the NVIDIA Jetson AGX Xavier chipthat is used in modern ADAS systems in the automotive domain, comprises 2 DLAs (Deep Learning Accelerators), 1 integrated GPU (Graphical Processing Unit), and 8 ARM 57 processing cores. Efficiently programming ERTS for such hardware is not easy, as the complexity of the interaction between software and hardware resources makes it difficult to predict performance. Building predictable real-time applications on these platforms requires appropriate programming models. In the recent literature, many graph-based task models have been proposed to exploit the parallelism of such architectures 39, 24. Such models are neither based on components, nor are they parametric. It is our intention to investigate the possibility to apply component-based techniques to such complex task models.
3.1.2 Medium term
(A1.M1) Parametric scheduling analysis of Real-Time components.
Analyzing the schedulability of a system under variations of the task parameters is a complex problem: the complexity of the analysis grows exponentially with the size of the system, and it explodes for medium-to-large sized systems.
The problem can be decomposed by analysing the schedulability of smaller real-time components under variation of some parameters. The idea is to follow a Resource Reservation strategy, where components are assigned and guaranteed a fraction of the system resources. In this way, the temporal behaviour of one component is isolated from the interference of other components.
First, we will introduce the notion of parametric interface for a component modelled as a multi-rate data-flow program. The interface will specify the temporal properties and constraints on the input/outputs of a component: periodicity and deadline constraints, dimension of the buffer for communicating with other components, and communication protocols.
To analyse the schedulability of a components under the hypothesis of variation of its parameters (the ones specified in the interface as well as the WCET of the tasks), we will extend the sensitivity analysis techniques, first proposed by Bini et al. 26, 25 to more complex task models and to hierarchical scheduling systems. The objective is to find the range of the parameters for which the component is schedulable.
(A1.M2) Predictable communication costs.
ERTS are increasingly being built using multicore hardware. This transition is however still significantly delayed by the difficulty to provide safe and tight timing guarantees. Indeed, even though multicore architectures enable the simultaneous parallel execution of programs on different cores, these programs are not completely independent. They have to be synchronized at some point to exchange data and they also share some common resources, such as peripherals, communication bus and (parts of the) memory. Synchronizations and shared resource contentions cause hard-to-predict interferences and timing overheads, which significantly increase the complexity of timing analyzes (WCET and scheduling).
One solution for mitigating these overheads, and making them more predictable, consists in relying on multi-phase task models that decouple communication phases from computation phases 37, 29. This greatly simplifies WCET analysis of computation phases, and also makes it possible to schedule communication phases so as to reduce their interference.
Memory architectures based on local addressable memories (scratchpads), instead of caches, are also being proposed 30, 36, to avoid the hard-to-predict timing effects of cache consistency mechanisms (which are used to speed-up access to the main shared memory).
We plan to integrate these two approaches in our project, since predictability is a major concern. The Prelude compiler will be extended to provide multi-phase task code generation, to be executed on scratchpad-based memory architectures. We will also develop the corresponding schedulability analysis method. Our objective is to devise our development framework such that the programmer abstracts from the implementation of communication mechanisms related on the target OS and hardware. This will enable the programmer to seamlessly transition between different architectures (unicore/multicore, cache-based/scratchpad-based).
3.2 Axis 2: Static Analysis of RT components
In this research axis, we will design static program analysis techniques for RT components at the binary level. While these techniques will mainly focus on WCET analysis, some results will also be reused to analyze security properties instead.
3.2.1 Short Term
(A2.S1) Symbolic WCET analysis.
We will work towards improving static analysis techniques for Worst-Case Execution Time Analysis. In particular, we will extend the Parametric WCET method 23 with more powerful symbolic capabilities. Currently, Parametric WCET can represent the WCET of a function as a formula in a number of parameters (e.g. input data). It does however suffer from two important limitations. First, it cannot represent relations between distinct parameters. We will extend the Parametric WCET by abstract interpretation of binary code to detect linear relations between distinct parameters in the code, by using techniques similar to 22. Second, it struggles to represent program properties that relate instructions of the program that are not close to one another, such as for instance infeasible execution paths 38. We are currently extending this work to enable the representation of properties related to such global execution contexts.
3.2.2 Medium Term
(A2.M1) Modular WCET analysis
Traditional WCET analysis is performed on a whole program. This approach is limited by two factors: first, performance concerns (analysis time tends to grow faster than the analyzed program size), and second, the analysis requires access to the complete program (including libraries, etc.). A modular and composable WCET analysis approach would reduce the analysis time, and enable the integration of third-party library or system calls in the analysis process.
To this end, we want to extend our polyhedra-based abstract interpretation 22 to support inter-procedural analysis, based on function summaries 28, describing relations between the inputs and outputs of the function. This will enable us to compute WCET-related functional properties, such as e.g. loop bounds, in a composable way.
This work on composable analysis will lead to a full composable WCET analysis, by integrating it in our symbolic WCET computation framework 23.
Dependencies: To achieve this objective, we will need the advanced parameter handling techniques of A2.S1.
(A2.M2) Security analysis of binary code
Program analysis of ERTS has historically focused mainly on safety, i.e. ensuring the absence of system failures. However, in recent years ERTS have become increasingly more connected to other computer systems through communication networks. This makes ERTS more vulnerable to external attacks, as illustrated by various reports of hacks of highly computerized modern cars. This results in an increased need for analyses that focus on ensuring the security of ERTS, i.e. ensuring there is no vulnerability to external malevolent computer attacks.
Our work on abstract interpretation of binary code 22 enables to detect linear relations between the data-locations accessed by a binary program (registers, memory addresses and their contents). While this work was initially targeted for WCET analysis, we plan to apply the developped techniques to the security domain as well. In particular, we will analyze security properties specific to the binary structure (e.g. unauthorized accesses to specific memory sections) and study the discovery of potential security threats in closed-source software (to detect malwares).
3.3 Axis 3: Proof of RT Components
The formal proof activity in the project will focus on compositional techniques for proving RT components of operating systems. Our plan is to focus mainly on RT schedulers.
3.3.1 Short term
(A3.S1) A proof methodology for a standard scheduling policy
We shall start with the standard scheduling policy EDF (Earliest Deadline First) and develop a proof methodology for it, which we shall later adapt to more advanced policies. The methodology incorporates a formal notion refinement as a means to master complexity and to smoothly descend from abstract definitions down to executable schedulers.
First, we are planning to model EDF at an abstract level in Coq. We shall formally prove at this level the schedulability property: under adequate hypotheses any given set of periodic hard real-time tasks can be scheduled, such that each task completes before its deadline. Since in the short term we shall only deal with strictly periodic, hard real-time tasks (reading data from sensors, performing some computation and sending the results to actuators), one only needs to consider the schedulability on finite executions, whose length equals the hyper-period: the least common multiplier of the task's periods. As a result, we expect that induction, well supported by Coq, will be the appropriate proof technique for this stage of the project.
Then, we shall refine the abstract EDF scheduling policy into a scheduling algorithm written in Coq's input language Gallina, a purely functional language, and shall prove again by induction that the algorithm preserves the already established properties of the policy.
Next, our plan is to further refine these functional algorithms into imperative Gallina programs, in order to get a step closer to executable code1. Imperative programs in purely functional languages such as Gallina are traditionally written using monads e.g., state monads, which enable variable assignments in functional code. For doing this we shall benefit from the experience of our colleagues in the 2XS team, our closest collaborators within the CRIStAL laboratory. They have been developing a minimalistic OS kernel called Pip 41 in imperative Gallina using the state-monad technology and have directly proved properties of the kernel in Coq. Unlike them, we do not prove properties directly on the monadic code, but shall prove a refinement step (from functional to imperative) ensuring that schedulability holds on the imperative scheduler.
The final step is translating the imperative Gallina scheduler to executable code. For this we shall use a translator also developped by the 2XS team, which essentially maps word-for-word imperartive Gallina programs to C programs with appropriate primitives that, after compilation of the C code, turn our schedulers into executable programs within Pip.
3.3.2 Medium term
In the medium term we are planning to make progress on two directions: the RT components being proved and the proof techniques.
(A3.M1) More advanced schedulers and other RT components
Once the validation of the proof/refinement methodology on the EDF example is complete, we are planning to progressively generalise it to other schedulers. The next likely candidate is the Grub scheduler, developped by Giuseppe Lipari 21, 32, which generalises EDF and makes it possible to mix periodic tasks (hard real-time) with sporadic tasks (soft real-time). The algorithm guarantees that the deadlines of the hard real-time tasks are met, while for the soft real-time ones a certain quality of service is guaranteed.
We are also planning to formally verify existing resource reservation hierarchical schedulers 33 by extending the proof/refinement approach with compositional features that exploit the component-based nature of the considered applications.
Depending on the availability of human resources, we would also like to formally verify other RT components, such as interruption multiplexers, memory managers, or synchronisation mechanisms.
(A3.M2) More advanced proof techniques
We expect that different verification techniques will be necessary to prove these more advanced schedulers. The EDF scheduler can be proved correct by considering its behaviour over a limited period of time, which as explained above can be dealt with using induction. However, Grub also has to schedule sporadic tasks that, by definition, do not repeat themselves periodically. Without a periodic repetition the behaviour cannot be studied over a finite interval, infinite executions have to be considered. Hence, we are planning to use coinduction, the natural technique for defining and reasoning about infinite objects. As stated in the Preliminaries we already have experience with coinduction, especially, with improving the way it is dealt with in Coq to make it better suited for use in nontrivial applications. We are planning to continue doing this both for corecursive program definitions (e.g., reactive systems, including schedulers, are such programs) and for coinductive reasoning techniques.
3.4 Long term
In the long term, we will integrate the elements studied during the medium term phase, in order to provide a seamless framework that goes from high-level design to final implementation. Translations will be automated and proved correct. These objectives are transverse by nature, so all members of the project-team will participate. Since these objectives focus on integration of our previous results, they are related to all of our short and medium term objectives.
(L1) Integrated framework
During the medium term phase, we will develop bricks that contribute to the design and analysis of ERTS. In the long term phase, we will integrate these bricks into a complete framework. This will raise several research topics.
First, we will have to evaluate the impact of scheduling on WCET analysis. Though this topic has already been studied before, our symbolic approach to both problems will raise new opportunities and challenges.
Second, we will evaluate the scalability of the approach with respect to realistic and complex real-time programs. In particular, the advent of powerful heterogeneous hardware platform permits to exploit their large scale parallelism. It is then important to check the suitability and the expressiveness of our framework with respect to these new powerful platforms.
(L2) Proving semantics preservation
In our framework, an ERTS is first specified with a high-level data-flow semantics (in Prelude). Then, it undergoes translations to produce the final program (in C) embedded on the hardware platform. One of our long term objectives is to prove that the complete translation process, from Preludeto C, is semantics-preserving.
There exists previous work and techniques for the formal verification of compilers such as CompCert 31 (from C code to binary code) and the Lustre verified compiler 27. However, these works focus on the preservation of the functional semantics (computing the correct values). A major novelty of our work will be to focus on the preservation of the temporal semantics (computing values at the correct time) as well. As far as we know, proving the preservation of temporal semantics was previously explored in theoretical models (e.g. timed automata, or Petri nets), but not in programming languages and compilers. It is an ambitious challenge, because it connects compilation with scheduling and WCET analysis.
(L3) Corecursion-preserving compilation and coinductive verification techniques
An alternative view of reactive programs (such as Prelude programs) is that of corecursive transformers from infinite flows of inputs to infinite flows of outputs. We envisage an enhanced compilation chain that, in addition to what is planned in L2, enables the tracing of corecursion down to the executable code. Since corecursive calls typically compile to low-level instructions such as loops or jumps, such a tracing mechanism would enable recognising the corecursive calls at the low-level. This, in turn, would enable the formal reasoning about low-level corecursive programs, using coinductive techniques that we shall develop in A3. We note that schedulers can also be expressed as corecursive programs, hence the verification boils down to compositionally verifying compositions of corecursive programs. It is, again, an ambitious challenge at every step, since corercursive programs are notoriously difficult to define, compose, and verify. This envisaged works depends on progress in essentially all the objectives enumerated above.
(L4) Dynamic update of components
ERTS may evolve over time, in particular, one component may be upgraded while the system is operational. In the traditional development process of critical software, once the system has been developed, tested and certified, it is not possible to change it anymore, with the only exception of correcting a critical bug. Dynamic updates are not possible since they would require to re-certify the whole system.
In the long term, we would like to apply our component based development process to the problem of guaranteeing the correctness of dynamic updates. This means that the system must be able to evolve over time, during operation, without jeopardizing the guarantee on existing properties.
Given the large complexity of the formal methods we will use for off-line analysis, it is unthinkable to apply the same type of analysis on-line. One possibility is to separate the analysis into two distinct parts: an off-line part which may be complex and does most of the work; and an on-line part which is much simpler but relies on the off-line computation. Alternatively, it is possible to off-load part of the analysis to the cloud, where there is abundance of computational resources.
4 Application domains
The long term research we propose to pursue in this project will advance the current development practice for embedded real-time critical systems.
First, it will impact the design and development of critical software for domains like avionics, automotive, train, etc. It is well known that developing safety-critical software is a long and costly process, where each error could endanger human life. It has been estimated that the cost to certify 30K lines of DAL A code is around 2M$ if the code has been developed by experienced programmers, and it jumps to 8M$ if the code has been produced by non-experienced ones.
The avionic industry is slowly adopting formal methods to reduce the cost by reducing (or, in certain cases, eliminating altogether) testing and improve confidence in the methodology. Our integrated framework (L1) will greatly reduce the development cost of safety-critical software because it will automatise many of the steps in the design and development methodology. For example, the use of semantic preserving transformations (L2, L3) will enhance the confidence in the correctness of the generated code, reducing the need for extensive testing, thus further reducing cost.
Other critical domains, like automotive, have not yet fully adopted safety-critical standard methodologies like in the avionic domain, mainly for cost reasons. Our framework will lower the cost of developing safety critical software, thus improving the safety of critical software in a wider range of domains.
Finally, thanks to the research in (L4), it will be possible to update a software component on-line without performing a complete analysis of the system, while the system is operational. An example of futuristic application will be the possibility to update one software subsystem of an autonomous vehicle while the vehicle is running, without compromising its functionality.
5 Social and environmental responsibility
Raphaël Monat takes part in the gender-equality commission of the CRIStAL laboratory. There are no team-specific actions to promote diversity and gender balance. However, we adhere to the general policies of the CRIStAL laboratory and the Inria center of the University of Lille.
6 Highlights of the year
6.1 Awards
- Software-Verification Competition: in the “Software Systems” category, Mopsa earned the bronze medal in 2023 (first participation), and the gold medal in 2024.
- ETAPS 2024 best tool paper (117 articles at ETAPS) for our publication 15.
- FSCD 2024 best paper award by junior researcher obtained by Victor Sannier, for the article 17.
- Giuseppe Lipari has obtained the IUF nomination on the 1st October 2024.
7 New software, platforms, open data
7.1 New software
7.1.1 prelude
-
Keywords:
Synchorous language, Real time
-
Functional Description:
Prelude is a synchronous data-flow language with real-time constraints. Prelude programs are compiled into multi-thread C code. The language and its compiler are developed in collaboration with ONERA Toulouse.
- URL:
- Publications:
-
Contact:
Julien Forget
-
Partner:
Onera
7.1.2 ptask
-
Keywords:
Real time, Library
-
Functional Description:
PTASK is a library for programming real-time systems in Linux. It serves as the target RTOS API in the SYCOMORES project. The PTASK library is authored by Giuseppe Lipari. It has been initially developed to support teaching real-time systems at the Scuola Sant’Anna. It has later been extended with additional capabilities and it is being used as target for design tools such as CPAL19 from RTaW20 and by other companies.
- URL:
-
Contact:
Giuseppe Lipari
-
Partner:
Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna
7.1.3 Catala
-
Keywords:
Domain specific, Programming language, Law
-
Functional Description:
Catala is a domain-specific programming language designed for deriving correct-by-construction implementations from legislative texts. Its specificity is that it allows direct translation from the text of the law using a literate programming style, that aims to foster interdisciplinary dialogue between lawyers and software developers. By enjoying a formal specification and a proof-oriented design, Catala also opens the way for formal verification of programs implementing legislative specifications.
- URL:
- Publications:
-
Contact:
Denis Merigoux
-
Participants:
Vincent Botbol, Romain Primet, Denis Merigoux, Louis Gesbert, Aymeric Fromherz, Alain Delaet-Tixeuil, Raphael Monat
-
Partner:
Université Panthéon-Sorbonne
7.1.4 dates-calc
-
Keywords:
Law, Programming language
-
Functional Description:
A date calculation library with a well-defined semantics
- URL:
- Publication:
-
Contact:
Raphael Monat
7.1.5 Mopsa
-
Keywords:
Formal methods, Static analysis, Abstraction
-
Functional Description:
Mopsa is an open-source static analysis platform relying on abstract interpretation. It provides a novel way to combine abstract domains, in order to offer extensibility and cooperation between them, which is especially beneficial when relational numerical domains are used. It is able to analyze C, Python, and programs mixing these two languages. Mopsa was originally developed at LIP6, Sorbonne Université following an ERC Consolidator Grant award to Antoine Miné. It is now partially developed at Inria.
- URL:
-
Contact:
Antoine Mine
-
Partner:
Sorbonne Université
7.1.6 Haddock
-
Keywords:
Partial function, (Co)Recursive Function, Coq
-
Functional Description:
A Coq library for defining and reasoning about partial (co)recursive functions.
- URL:
-
Contact:
Vlad Rusu
-
Partners:
Université de Lille, CNRS, Université de Bucarest
7.1.7 Polymalys
-
Keywords:
Abstract interpretation, Polyhedra
-
Functional Description:
Polymalys is a tool for static analysis of binary code. It discovers linear relations between data locations (i.e. memory locations as well as registers) of the code. The analysis relies on abstract interpretation using a polyhedra-based abstract domain. The current main application is Worst-Case Execution Time analysis in combination with the WSymb tool.
- Publications:
-
Contact:
Julien Forget
7.1.8 WSymb
-
Name:
Symbolic Worst-case execution time computation
-
Keywords:
WCET, Real time
-
Functional Description:
WSymb is a WCET analysis tool. Its main specificity is that, instead of a constant WCET, it computes a *WCET formula*, where symbols (or parameters) can correspond to various values unkown at analysis time. The formula can later be instanciated, when parameter values are known.
- URL:
- Publications:
-
Contact:
Julien Forget
7.1.9 Seplog
-
Keywords:
Separation Logic, Coq
-
Functional Description:
Seplog is a separation logic for GallnaC, a shallow embedding of an imperative, pointer-manipulating language in the Coq proof assistant.
- URL:
-
Contact:
Vlad Rusu
-
Partners:
CNRS, Université de Lille
8 New results
8.1 Mopsa at the Software Verification Competition
Mopsa is a multilanguage static analysis platform relying on abstract interpretation. It is able to analyze C, Python, and programs mixing these two languages.
In Fall 2023, Raphaël Monat participated to the Software Verification Competition (SV-Comp) by submitting the Mopsa static analyzer he is co-developing. Mopsa earned a gold medal in the SoftwareSystems category; this category aims at "representing verification tasks from real software systems". There were 22 competing tools.
This second participation is described in 16.
Participants: Raphaël Monat.
8.2 Formalizing Date Arithmetic and Statically Detecting Ambiguities for the Law
Legal expert systems routinely rely on date computations to determine the eligibility of a citizen to social benefits or to check that an application has been filed on time. Unfortunately, date arithmetic exhibits many corner cases, which are handled differently from one library to the other, making faithfully transcribing the law into code error-prone, and possibly leading to heavy financial and legal consequences for users. In this work, we aim to provide a solid foundation for date arithmetic working on days, months and years. We first present a novel, formal semantics for date computations, and formally establish several semantic properties through a mechanization in the F* proof assistant. Building upon this semantics, we then propose a static analysis by abstract interpretation to automatically detect ambiguities in date computations. We finally integrate our approach in the Catala language, a recent domain-specific language for formalizing computational law, and use it to analyze the Catala implementation of the French housing benefits, leading to the discovery of several date-related ambiguities.
This work 15 has been extremely well received and awarded “best ETAPS tool paper” (among 117 ETAPS papers in total).
Participants: Raphaël Monat.
8.3 Contention-free scheduling of AECR dag tasks on partitioned multicore platforms
This work is based on the thesis of Ikram Senoussaoui. She is supervised by Giuseppe Lipari, Kamel Benahoua (University of Oran 1) and Houssam Zahaf (University of Nantes).
Commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) platforms feature several cores that share and contend for memory resources. In real-time system applications, it is of paramount importance to correctly estimate tight upper bounds to the delays due to memory contention. However, without proper support from the hardware (e.g. a real-time bus scheduler), it is difficult to estimate such upper bounds.
We aim at avoiding contention for a set of tasks on a hardware multicore architecture, where each core has its private scratchpad memory and all cores share access to the main memory. By avoiding contention, we make multicore programming predictable again.
We propose a new task model, AECR-dag (Acquisition, Execution, Communication Restitution – Directed Acyclice Graph), where a periodic or sporadic task is modeled by a set of subtask nodes and communication between then, organised as a DAG. The model captures the parallelism of the task and it makes explicit the communication between the subtasks.
Then, we propose a methodology based on Integer Linear Programming, for allocating the subtasks on the cores using partitioned preemptive EDF, so to reduce the cost of communication between subtasks allocated to different cores. Then, we propose a method based on Evolutionary Programming, that allocates the intermediated deadlines to the subtasks so to respect the precedence constraints and the end-to-end deadline.
This work has been presented in the last chapter of the thesis of Ikram Senoussaoui. She defended succesfully in December 2023. The same work has been published in the Journal Of System Architecture 12.
Participants: Giuseppe Lipari, Ikram Senoussaoui.
8.4 Scheduling multiple kernels on GPUs
GPUs are powerful computing architectures that are increasingly used in embedded systems for implementing complex intelligent applications. Unfortunately, it is difficult to predict their temporal behavior, especially when multiple parallel tasks are concurrently executed. Running one single task at a time may results in severe underutilization of the resources; on the other hand, running multiple tasks concurrently may introduce mutual interference.
We propose the Parallel Batch Scheduler (PBS) to enable parallel execution of a set of real-time tasks on GPUs. PBS avoids concurrent execution when it might jeopardize schedulability, and it identifies scenarios where parallel flows might enhance platform utilization and therefore schedulability. To find the feasible scenarios, we propose a scheduling analysis based on a scheduling graph, in which all possible concurrent and serialized scenarios are evaluated for schedulability. To mitigate the explosion in the state space, we propose a technique to reduce the size of the graph.
This work is part of the thesis of Nordine Feddal, directed by Giuseppe Lipari. The work has been presented in the International Conference on Real-Time Networks and Systems 14.
Participants: Nordine Feddal, Giuseppe Lipari.
8.5 WCET analysis with procedure arguments as parameters
In 10 we present a methodology for obtaining the WCET of a program procedure as a function of the its arguments. The methodology extends a previous method for symbolic WCET to the case of conditional statements (if-then-else). Then, a new technique based on abstract interpretation has been developed to 1) detect the arguments in the function code, 2) compute a symbolic expression of the WCET based on the arguments. Finally, a compiler generates efficient C-code for evaluating the formula at run-time, thus enabling the use for this technique for adaptive scheduling. The resulting methodology has been tested on several benchmarks from the literature, proving its efficiency and tightness.
This work is part of the thesis of Sandro Grebant. He was supervised by Julien Forget and Giuseppe Lipari, and he defended succesfully in November 2023.
Participants: Sandro Grebant, Julien Forget, Clément Ballabriga, Giuseppe Lipari.
8.6 Type systems for differential privacy
Differential privacy (DP) is a quantitative statistical notion of privacy that provides strong confidentiality guarantees and at the same time is flexible enough to allow for useful computations on private data. Technically it relies on the notion of program sensitivity, which is a bound relating the distance between two outputs of a program to the distance between the two inputs. The idea of DP is to insert random noise at suitable positions in the program so that the result does not depend on the presence of a single individual in the database and at the same time is close enough to the real value. DP has become a gold standard for data privacy, but manually checking that large programs are differentially private can be both tedious and subtle. For this reason some formal methods approaches to sensitivity analysis and DP have been developed. In particular a type system for a functional language called Fuzz, based on linear logic, had been introduced in 2010 by Reed and Pierce and ensures that a well-typed program is differentially private. However, it could only handle a specific metric on vectors and lists, the L1 metric. This is a limitation for using certain noising mechanisms or certain operations on matrices that require other Lp metrics. In a previous work in collaboration with colleagues of Boston University we had proposed an extension of this language, called Bunched Fuzz, where product types and lists are generalized to arbitrary Lp distances, together with a denotational semantics. This type system used bunches inspired from the logic of bunched implications. As part of V. Sannier’s PhD thesis we proposed another variant of this system which keeps the ability to handle Lp distances but has a simpler system of rules and enjoys better operational properties 17.
Participants: Patrick Baillot, Victor Sannier.
8.7 Characterization of type-2 feasible functionals in term-rewriting
Complexity classes such as the class FP of polynomial time functions are classically defined by Turing machines with resource restrictions but several works in the literature have characterized equivalently the class FP in the term-rewriting framework as the class of functions representable by terms admitting certain interpretations as functions on integers. The class of basic feasible functionals (BFF) is the analog of FP for type-two functionals, that is, functionals that can take functions as arguments. BFF can be defined by means of oracle Turing machines of time bounded by a second-order polynomial. We addressed the problem of characterizing the class BFF by higher-order term rewriting and showed in [16] that the class BFF is the class of functionals that can be represented by higher-order terms admitting a certain notion of cost-size tuple interpretations.
Participants: Patrick Baillot.
8.8 An algebraic approach for the verification of probabilistic imperative programs.
Kleene algebras with tests (KAT) are an algebraic approach for reasoning on imperative programs with equational proofs, which has been shown by Kozen to be as expressive as propositional Hoare logic. We have proposed in 18 an extension of KAT for reasoning on imperative programs with probabilistic primitives. Our system can prove that a probabilistic program satisfies a given postcondition except with a given probability. We have proved that it is as expressive as a probabilistic variant of propositional Hoare logic from the literature (Union bound program logic). These results have been obtained as part of Leandro Gomes’ postdoc.
Participants: Patrick Baillot, Leandro Gomes.
8.9 Formal Definitions and Proofs for Partial (Co)Recursive Functions
Participants: Vlad Rusu.
The Coq proof assistant has a rich specification language (Gallina), which, for all its qualities, is still lacking in certain aspects. It only has total functions, which limits its use for certain applications we develop in the team. In particular:
- total recursive functions cannot model while loops: the latter may not terminate, but the former must terminate. The absence of loops required us to use application-dependent tricks in earlier work. A clean solution requires while loops.
- total corecursive functions are not expressive enough for defining the semantics of our synchronous language Prélude. An infinite stream fed to the when instruction on a clock that is always absent is undefined, hence, when is a partial corecursive function.
In 9 we propose techniques for defining and reasoning about partial (co)recursive functions in Coq. In particular, we provide solutions to the above-mentioned practical problems. Specifically, we have formalized in the Coq proof assistant the subset of domain theory used for defining and reasoning about partial (co)recursive functions. For the functions that are actually total, a coinductive proof technique enables users to prove the totality. We present several examples of partial recursive and corecursive functions defined with our approach. In particular, we incorporate while loops in Gallina, and provide while-loops with a Hoare-logic rule which, together with the other rules for the other instructions of the language, can be used for reasoning about programs. Finally, we have extended the Hoare logic into a separation logic for reasoning about low-level code - imperative programs with pointers, written in the GallinaC language briefly described below.
8.10 GallinaC
Participants: Vlad Rusu.
GallinaC is simultaneously the name of a simple but expressive imperative language for low-level programming, and that of a project around this language, currently work-in-progress in collaboration with David Nowak and Frédéric Fort from the 2XS team. The project is funded by IPCEI-CIS, a large European initiative around the continuum cloud-edge-IoT. The GallinaC project aims at defining a proved-correct translation from the GallinaC language to the subset of C supported by the Compcert compiler. Here, correctness means that the semantics of GallinaC is preserved when translated to Compcert C; in particular, all Separation Logic assertions proved on GallinaC programs still hold on their respected translations to C. Some original features of our approach with respect to the state of the art (VST, Iris, ...) include a combination of a shallow embedding of GallinaC in Coq (for scalable proofs in Separation Logic) with a deep embedding suitable for proving the correctness of the translation to C.
9 Partnerships and cooperations
9.1 International initiatives
9.1.1 International Emerging Action CNRS: Formal methods for probabilistic programs and differential privacy (FMPDP)
This is an exchange project with Boston University (MA, US) funded by CNRS for 2025 and 2026 (11k€), led by P. Baillot, on the topic of formal methods for differential privacy, including type systems, program logics and algebraic methods. It will fund three visits of members of the team to Boston University and three visits of researchers or PhD student of this University to Lille.
Participants: Patrick Baillot, Leandro Gomes, Victor Sannier.
9.2 International research visitors
9.2.1 Visits of international scientists
Inria International Chair.
On 17 October 2024, we received Sarah Lawsky, Inria International Chair embedded within Prosecco (Paris), and Aymeric Fromherz, ISFP in Prosecco team, to discuss how automated verification techniques could integrate within legislative processes.
Participants: Raphaël Monat, Pierre Goutagny.
9.3 National initiatives
9.3.1 Inria Exploratory Action AVoCat
Raphaël Monat is co-PI of an Inria Exploratory Action called AVoCat, aiming at exploring Automatic Verification of Catala programs. The project is shared with Aymeric Fromherz at Inria Paris.
Participants: Raphaël Monat.
9.3.2 ANR JCJC RAISIN: Resource-Aware Conservative Static Analysis
Raphaël Monat has been granted an ANR JCJC, starting January 2025. Additional members: Julien Forget, and Sophie Cerf (researcher at Inria Lille). This grant is funded by the National Research Agency, through a call open to early-career permanent researchers. It will fund a PhD student and a postdoc to work on Resource-Aware Conservative Static Analysis.
Participants: Raphaël Monat, Julien Forget.
9.3.3 ANR PRC HOPR: Higher-Order Probabilistic and Resource-aware Reasoning
(01/01/2025-31/12/2029). Coordinator: Patrick Baillot. Inria Lille/CRIStAL; Inria Paris; Inria Sophia-Antipolis; IRISA Rennes. Total funding: 479kE. This project deals with logical frameworks for reasoning on cryptographic constructions and on privacy protection. It aims at improving proof-assistants for these purposes by extending logical frameworks with the possibility of handling higher-order computation, probabilistic reasoning and complexity-bounded computation. These progresses will be used in cryptography to improve the proof-assistants Squirrel and Easycrypt. In privacy the project will develop new program logics for reasoning on differential privacy and combining program logic with typing.
Participants: Patrick Baillot, Leandro Gomes, Victor Sannier.
10 Dissemination
10.1 Promoting scientific activities
10.1.1 Scientific events: organisation
General chair, scientific chair
- Julien Forget was the General Chair of the ECRTS 2024 conference in Lille on July 2024, one of the major conferences in the domain. The conference attracted more than 100 participants from all over the world.
Member of the organizing committees
10.1.2 Scientific events: selection
Chair of conference program committees
- Raphaël Monat co-chaired the SOAP 2024 workshop (co-located with PLDI 2024). He co-chaired the artifact evaluation of the ECOOP 2024 conference.
Member of conference program committees
- Raphaël Monat was PC member of the national conference JFLA, and of the following international workshops: NSAD, DEBT.
- Giuseppe Lipari was member of the PC of ECRTS 2024.
Steering committee
- Patrick Baillot has been steering committee chair of FSCD since 2024.
10.1.3 Journal
Member of the editorial boards
- Giuseppe Lipari is member of the editorial board of the Real-Time System Journal;
- Giuseppe Lipari is member of the editorial board of the Journal of Systems Architecture.
10.1.4 Invited talks
- Patrick Baillot : A Kleene algebra with tests for union bound reasoning about probabilistic programs, AMS-UMI International Joint Meeting 2024, Palermo (Italy), July 23-26, Proof-Theory and Theoretical Computer Science, Special Session.
10.1.5 Research administration
- Patrick Baillot is a scientific advisor (Délégué scientifique) at CNRS Sciences Informatiques, for section 06, since 9/2022 (40% of his working time).
10.2 Teaching - Supervision - Juries
10.2.1 Teaching
Giuseppe Lipari was responsible for the "IoT and Cybersecurity" specialty of the Master in Computer Science of the University of Lille until August 2024. The Masters' courses of this specialty are taught in English. The specialty is also part of the Graduate Programme "Information and Knowledge Society" of the University of Lille.
Giuseppe Lipari taught the following courses at the University of Lille in the academic year 2023-2024:
- Programmation de Systemes (Resp., L3, 3 ECTS, 180 students) and Programmation de Systemes + (Resp., L3, 3 ECTS, 80 students)
- Embedded System Design (Resp., M1, 6 ECTS, 25 students)
- Operating System 1 (M1, 3 ECTS, 25 students)
- Operating Systems 2 (Resp., M1, 3 ECTS, 75 students)
- Advanced Object Oriented Programming (Resp., M1, 3 ECTS, 75 students)
- Advanced Operating Systems (Resp., M2, 3 ECTS, 30 students)
- Real-Time Systems (Resp., M2, 3 ECTS, 15 students)
Moreover, Giuseppe Lipari supervised several internships and memoirs of M2, for a total service of 338.5 hours (eqTD) in 2023-2024.
Julien Forget taught the following courses at the University of Lille in the academic year 2023-2024:
- Structured programming (Resp., Ing3, 48h, 50 students)
- Operating Systems (Ing3, 16h, 12 students)
- Operating Systems (Resp., Ing3, 16h, 50 students)
- Object-oriented Programming (Ing4, 10h, 12 students)
- Theoretical Computing (Resp., Ing4, 22h, 24 students)
- Data structures (Resp., Ing3, 12h, 24 students)
- Programming project (Ing3, 22h, 12 students)
- An Introduction to Research (Ing4, 6h, 50 students)
Overall, the teaching activities of Julien Forget amount to a total service of 245 hours (eqTD) in 2023-2024.
Vlad Rusu taught a course on Formal Methods for Embedded Systems (M2) at the "Internet of Things and Cybersecurity" specialty of the Master in Computer Science at the University of Lille (M2, 12 hours).
Vlad Rusu gave a one-day course on introduction to the Coq proof assistant at an autumn school (September 2024, Bucharest, Romania).
Raphaël Monat taught a course on "Compilation des Logiciels" at the Master in Computer Science of the University of Lille (M1, 3 ECTS, 24 hours). He was also invited to give a practical session on the Mopsa static analyzer at the International Lipari Summer School on Abstract Interpretation.
10.2.2 Supervision
- Romit Roy Chowdhury (Chennai Mathematical Institute, India): 2-month L3 research internship (may-july 2024), on Polynomial time computation in the Pi-calculus, supervised by Patrick Baillot , supported by CNRS ReLAX grant and internship programme.
10.2.3 Juries
Raphaël Monat has been a jury member for oral computer science exams to enter Écoles Normales Supérieures.
Giuseppe Lipari has been president of the PhD jury of Mohamed-Amine Khelassi, at Université Gustave Eiffel on December 17 2024.
Julien Forget has been an examiner for the defense of Guillaume Roumage's Ph.D. (Université Paris Saclay/CEA-List) on "Timing Analysis of Mode-Dependent Cyber-Physical Systems under Relaxed Real-time Constraints".
11 Scientific production
11.1 Major publications
- 1 inproceedingsNew challenges in adaptive real-time systems with parametric WCET.RTSOPS 2023 - 12th International Real-Time Scheduling Open Problems SeminarVienne, AustriaJuly 2023HAL
- 2 articleRelational abstract interpretation of arrays in assembly code.Formal Methods in System DesignOctober 2022HALDOI
- 3 articleReducing the fault vulnerability of hard real-time systems.Journal of Systems Architecture133December 2022, 102758HALDOI
- 4 articleFormal Definitions and Proofs for Partial (Co)Recursive Functions.Journal of Logic and Algebraic Methods in Programming141October 2024, 27HALDOI
- 5 inproceedingsWCET analysis with procedure arguments as parameters.RTNS 2023: The 31st International Conference on Real-Time Networks and SystemsDortmund, GermanyACM2023, 11-22HALDOI
- 6 inproceedingsFormalizing Date Arithmetic and Statically Detecting Ambiguities for the Law.Lecture Notes in Computer ScienceESOP 2024 - 33rd European Symposium on Programming14577Lecture Notes in Computer ScienceLuxembourg City, LuxembourgSpringer Nature SwitzerlandApril 2024, 421-450HALDOI
- 7 inproceedingsA Formal Correctness Proof for an EDF Scheduler Implementation.Proc. 28th IEEE Real-Time and Embedded Technology and Applications SymposiumRTAS 2022: 28th IEEE Real-Time and Embedded Technology and Applications SymposiumMilan, ItalyMay 2022HALDOI
- 8 inproceedingsBunched Fuzz: Sensitivity for Vector Metrics.ESOP 2023 - European Symposium on ProgrammingProceedings of ESOP 2023 (European Symposium on Programming)Paris, FranceSpringerApril 2023HALDOI
11.2 Publications of the year
International journals
International peer-reviewed conferences
Reports & preprints
11.3 Cited publications
- 20 miscSCADE Suite.2018back to text
- 21 articleResource Reservations for General Purpose Applications.IEEE Trans. Ind. Informatics512009, 12--21URL: https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2009.2013633DOIback to text
- 22 inproceedingsStatic Analysis Of Binary Code With Memory Indirections Using Polyhedra.International Conference on Verification, Model Checking, and Abstract Interpretation (VMCAI'19)Lisbon, Portugal1 2019HALback to textback to textback to text
- 23 articleSymbolic WCET Computation.ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems (TECS)172December 2017, 1--26HALDOIback to textback to text
- 24 inproceedingsResource-Efficient Execution of Conditional Parallel Real-Time Tasks.Euro-Par 2018: Parallel ProcessingChamSpringer International Publishing2018, 218--231back to text
- 25 articleThe space of EDF deadlines: the exact region and a convex approximation.Real-Time Systems4112009, 27--51back to text
- 26 articleSensitivity analysis for fixed-priority real-time systems.Real-Time Systems391-32008, 5--30back to text
- 27 inproceedingsA formally verified compiler for Lustre.ACM SIGPLAN Notices526ACM2017, 586--601back to text
- 28 inproceedingsDisjunctive relational abstract interpretation for interprocedural program analysis.International Conference on Verification, Model Checking, and Abstract InterpretationSpringer2019, 136--159back to text
- 29 inproceedingsPredictable flight management system implementation on a multicore processor.Embedded Real Time Software (ERTS'14)2014back to text
- 30 inproceedingsCommunication Centric Design in Complex Automotive Embedded Systems.29th Euromicro Conference on Real-Time Systems (ECRTS 2017)Dubrovnik, Croatia2017back to text
- 31 miscThe CompCert C verified compiler.2018back to text
- 32 inproceedingsGreedy reclamation of unused bandwidth in constant-bandwidth servers.12th Euromicro Conference on Real-Time Systems (ECRTS 2000), 19-21 June 2000, Stockholm, Sweden, ProceedingsIEEE Computer Society2000, 193--200URL: https://doi.org/10.1109/EMRTS.2000.854007DOIback to text
- 33 inproceedingsResource Partitioning among Real-Time Applications.Proc. 15th Euromicro Conf. Real-Time SystemsIEEE Computer Society2003, 151--158DOIback to text
- 34 miscSimulink.2018back to text
- 35 articleMulti-task implementation of multi-periodic synchronous programs.Discrete Event Dynamic Systems2132011, 307-338back to textback to text
- 36 inproceedingsAutomated generation of time-predictable executables on multi-core.RTNS 2018October 2018back to text
- 37 inproceedingsA predictable execution model for COTS-based embedded systems.Real-Time and Embedded Technology and Applications Symposium (RTAS)IEEE2011back to text
- 38 inproceedingsA general approach for expressing infeasibility in implicit path enumeration technique.2014 International Conference on Embedded Software (EMSOFT)IEEE2014, 1--9back to text
- 39 articleParallel Real-Time Scheduling of DAGs.IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems251212 2014, 3242-3252DOIback to text
- 40 miscThe Coq proof assistant reference manual.2021back to text
- 41 miscThe Pip protokernel.2018back to text

