Section: Research Program
Modeling the dynamical response of biological systems with logical and (non)-linear constraints
As explained below, Answer Set programming technologies enable the identification of key controllers based on the integration of static data. As a natural follow-up, we also develop optimization techniques to learn models of the dynamics of a biological system. As before, our strategy is not to select a single model fitting with experimental data but rather to decipher the complete set of families of models which a compatible with the observed response. Our main research line in this field is to decipher the appropriate level of expressivity (in terms of constraints) allowing both to properly report the nature of data and knowledge and to allow for an exhaustive study of the space of feasible models. To implement this strategy, we rely on several constraint programming frameworks, which depend on the model scale and the nature of time-points kinetic measurements. The three following examples are shown in Fig. 2.
-
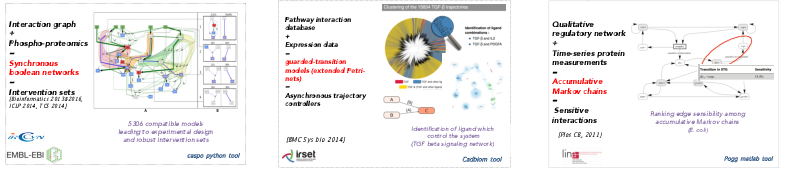
In [7], logical programming (Answer Set programming) is used to decipher the combinatorics ot synchrone boolean networks explaining static or dynamics response of signaling networks to perturbations (such as measured by phosphoproteomics technologies).
-
In [49], SAT-based approaches are used to decipher the combinatorics of large-scale asynchronous boolean networks. In order to gain in expressivity, we model these networks as guarded-transition network, an extension of Petri nets.
-
In [2] and [47], linear Programming frameworks are used to decipher the variability of the response of reaction-based networks. Still to gain in expressivity, we model systems with Markovian qualitative description of its dynamics together with quantitative laws which describe the effect of the dynamic transitions over higher scale quantitative measurements. Families of models are investigated with ad-hoc local search algorithms.
-
Finally, classical learning methods are used to build ad-hoc parameterized numerical models that provide the most parsimonious explanations to experimental measurements.
|