Section:
Scientific Foundations
Finite element methods for
interface problems
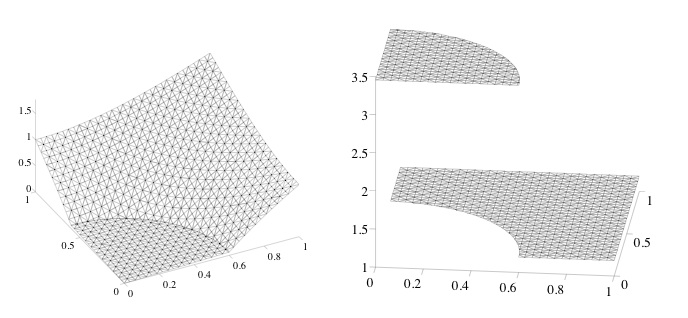
Figure
1. Incompressible elasticity with discontinuous material
properties (left: modulus of velocities, right: pressure; from
[40] ). |
The NXFEM (Nitsche eXtended finite element method) has been
developed in [62] and
[63] . It is based on a pure variational
formulation with standard finite element spaces, which are locally
enriched in such a way that the accurate capturing of an interface
not aligned with the underlying mesh is possible, giving a
rigorous formulation of the very popular XFEM. A typical
computation for the Stokes problem with varying, piecewise
constant viscosity is shown in Figure 1 . This
technology opens the door to many applications in the field of
fluid mechanics, such as immiscible flows, free surface flows and
so on.