Section: New Results
Discriminating brain microbleeds using phase contrast MRI in a multicentre clinical dataset
Participants : Takoua Kaaouana [Correspondant] , Marie Chupin, Didier Dormont, Ludovic de Rochefort, Thomas Samaille.
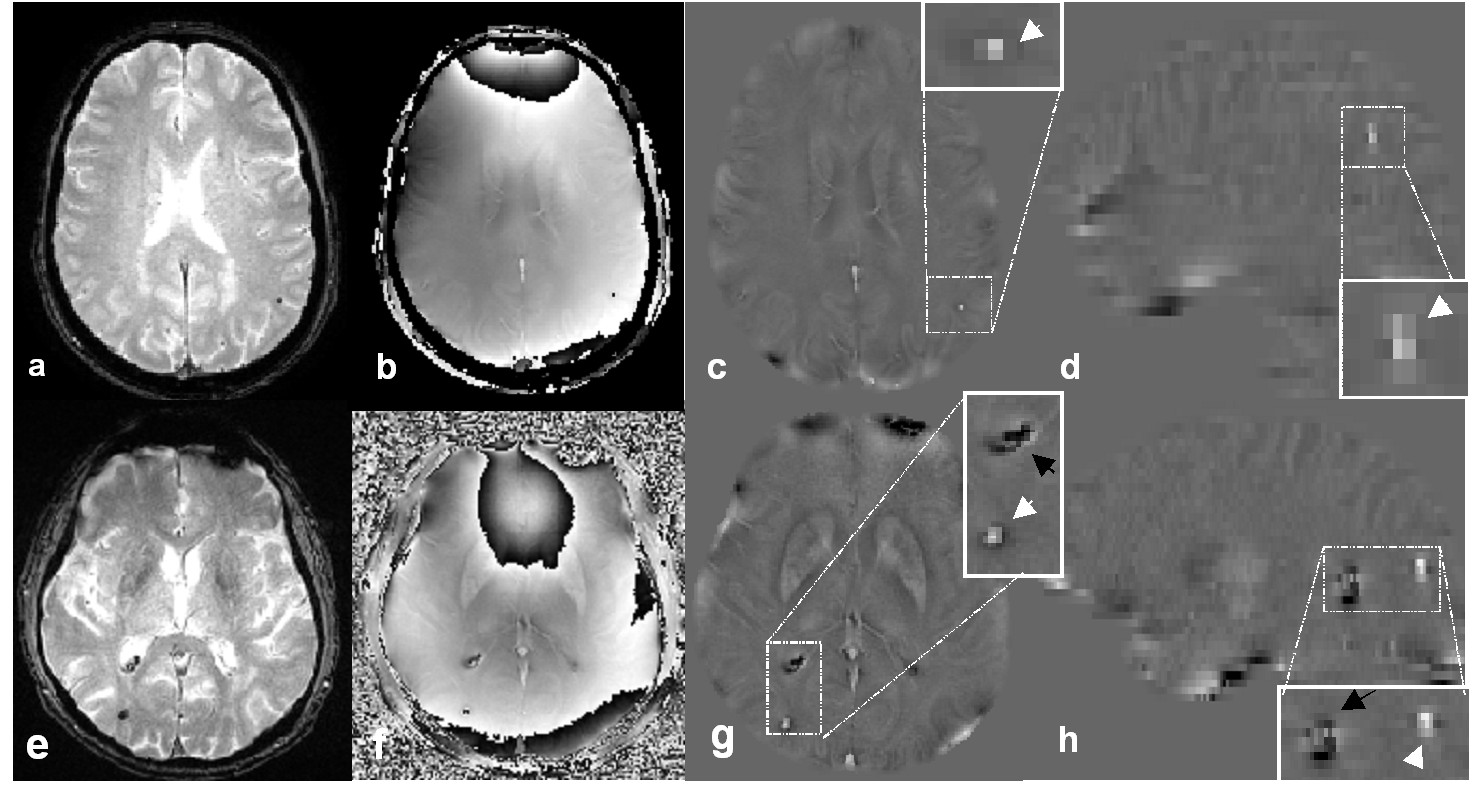
Brain microbleeds (BMBs) have emerged as a new imaging marker of small vessel diseases and they may play a crucial role in degenerative pathology such as Alzheimer's disease. Composed of hemosiderin, BMBs can be efficiently detected with MRI sequences sensitive to magnetic susceptibility (e.g. gradient recalled echo T2*W images). Nevertheless, that identification remains challenging because of confounding structures and lesions. Most T2*-weighted hyposignals result from local magnetic field inhomogeneity and can be identified either as BMBs, veins or brain micro-calcifications (BMCs). Differential diagnosis of BMBs and BMCs usually requires an additional CT scan. Quantitative susceptibility mapping techniques were proposed to discriminate between diamagnetic and paramagnetic structures, but they require a full 3D dataset and complex post-processing. We introduced a fast 2D phase processing technique including unwrapping and harmonic filtering thus yielding the internal field map, namely the field map generated only by sources within the volume of interest. We demonstrate its applicability and robustness on multicenter data acquired in standardized clinical settingand and its ability to discriminate between paramagnetic BMBs and diamagnetic BMCs through the use of the orientation of the dipolar pattern.
|
Related publications: [36] .