Section: New Results
Parallel Kelvin-Helhmohltz-like instability in edge plasma
Participants : Hervé Guillard, Boniface Nkonga, Marco Bilanceri, Giorgio Giorgiani.
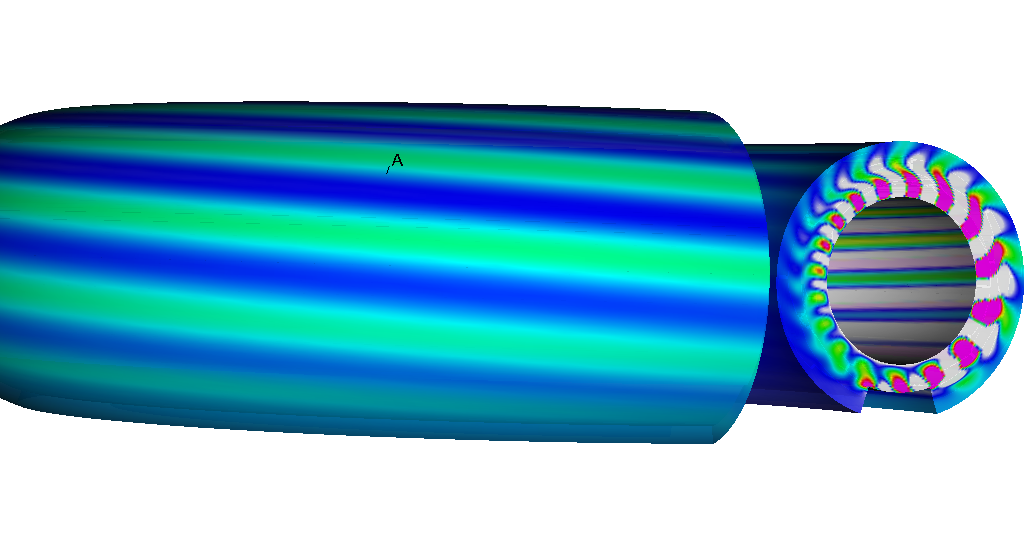
A large part of this year activities have been devoted to the investigation of the Kelvin-Helmholtz-like instabilities that can be triggered at the core/SOL transition, the sheath acceleration at the limiter or divertor plates leading to a radial shear for the velocity. Linear stability analysis developed in Schwander et al (Schwander et al., J. Nucl. Materials, doi:10.1016/j.jnucmat.2010.10.073 2011) actually reveals that unstable modes at the edge-core transition can develop in the presence of core rotation. This study was also an opportunity for a benchmarking comparison with the TOKAM3X code developed in IRFM and at Marseille. Both codes have confirmed the linear stability analysis and have shown that large fluctuations grow in the shear layer downstream of the limiter on the LFS (Low Field Side), the growth of these fluctuations being accompanied by a radial drift away from the limiter. Fig. 2 displays a 3D representation of these unstable density fluctuations. Apart from the physical results, this study has also shown the large sensitivity of the solutions to the discretization and to the implementation of the Bohm's boundary conditions. It has also shown that the study of these parallel KH like instabilities is a very demanding benchmark : these simulations require large meshes and since the growth rate of these instabilities is very weak, this results in an extremely long simulation time involving an extremely large number of time steps. In the future, it is planned to investigate the saturation of the instability as well as its possible presence in diverted plasmas.