Section: New Results
Parallel adaptively restrained particle simulations
Participants : Krishna Kant Singh, Stephane Redon.
We have continued our work on the development of parallel adaptively restrained particle simulations. We have integrated the ARPS algorithm in LAMMPS (Large-scale Atomic/ Molecular Massively Parallel Simulator). LAMMPS is a computationally efficient simulator, which contains a wide range of potentials and force fields for simulating systems like solid-state materials (metals, semiconductors), soft matter (biomolecules, polymers) and coarse-grained or mesoscopic systems.
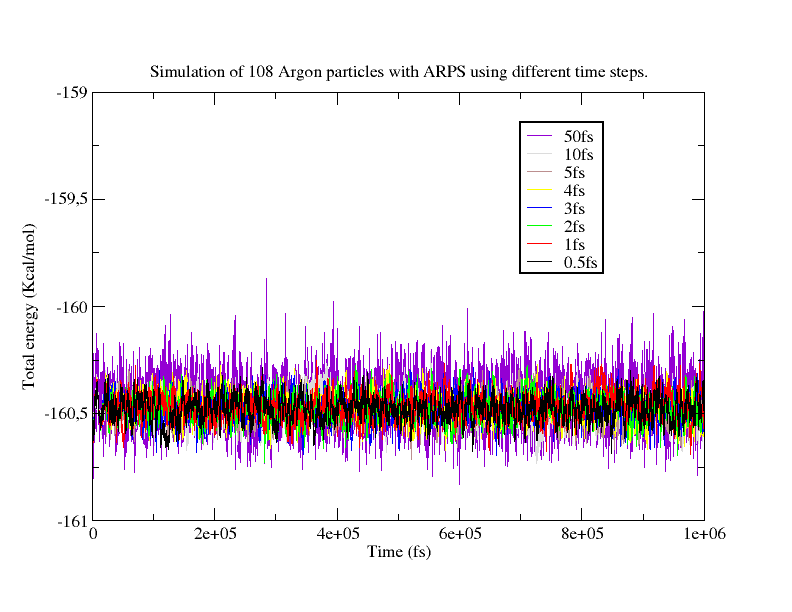
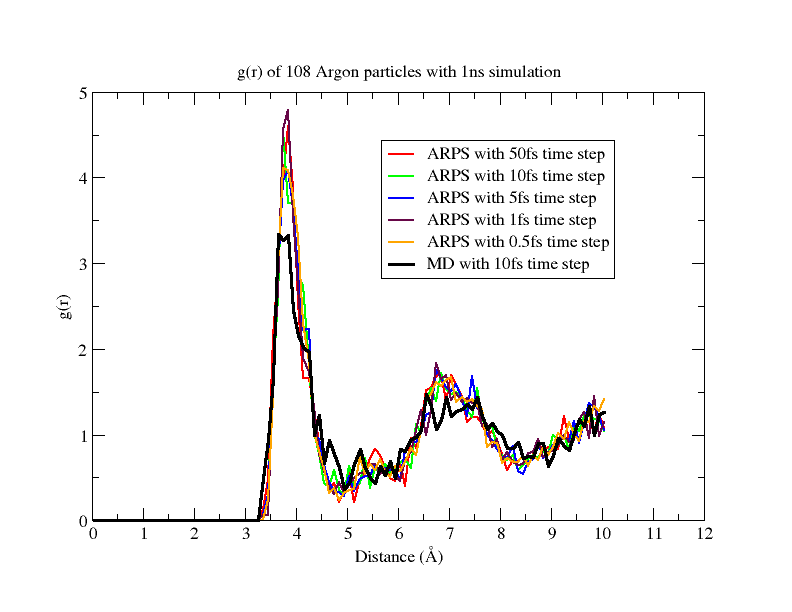
In order to verify our implementation of ARPS in LAMMPS, we have generated a trajectory of 1 ns by simulating 108 Argon particles using the ARPS algorithm and the NVE ensemble (constant Number of particles, Volume and Energy). All the particles were placed in an orthogonal box with a side length of angstrom. We used periodic boundary conditions with angstrom cut-off for the Lennard-Jones potential. We used a threshold for applying restraints and a threshold for releasing restraints. The system was simulated at different step sizes: using 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 50, 60, 70, 80 and 90 femtoseconds.
Our results show that ARPS in LAMMPS preserves the total energy during simulation (Figure 4 ) as well as the radial distribution function (Figure 5 ). We are now in the process of modifying the parallel force calculation algorithms in LAMMPS to make them incremental, i.e. make their cost proportional to the number of active particles in the simulation at a given time.