Section: New Results
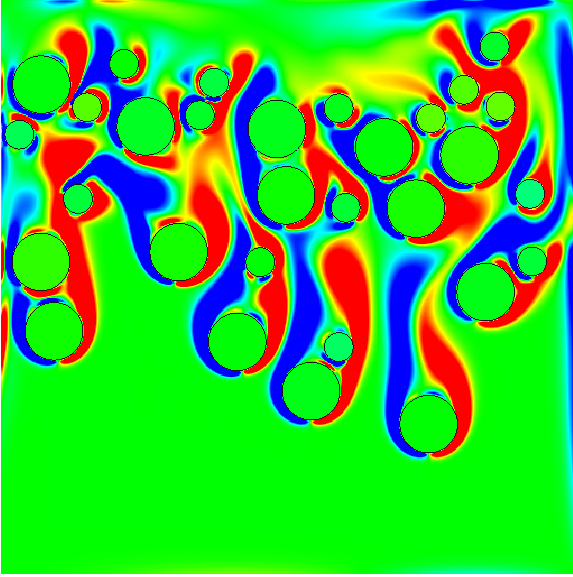
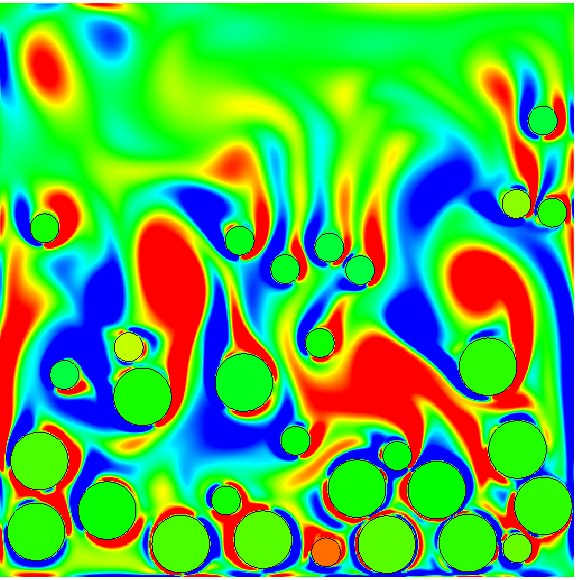
Particles flowing in a fluid
A new type of algorithm is designed to enable contacts efficiently between particles immersed in a fluid by adding a short range repulsive force. The algorithm is derived from the multi geometric deformable model introduced for image segmentation. It can handle multiple deforming bodies and avoid collision using a short range repulsive force depending on the distance to the closest interface. The main advantages of this method is it requires only five fields (three label maps and two distance functions) and one level set function to capture an arbitrary number of cells and it can, at the same time, deal with collisions.