Section: New Results
Density and repartition of cytoplasmic RNP (RiboNucleoprotein Particles) granules containing the Imp protein
Participants : Eric Debreuve, Xavier Descombes.
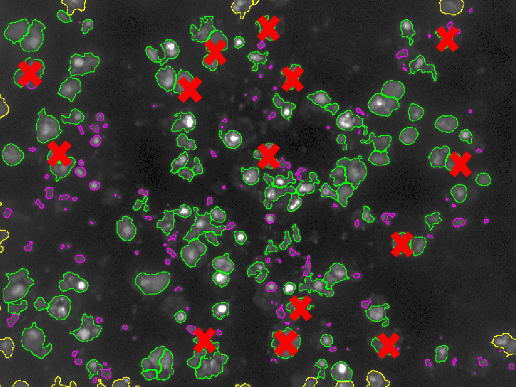
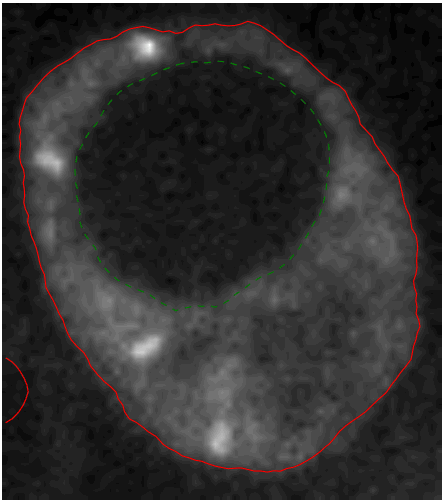
As part of the ANR project RNAGRIMP (Imp = IGF-II mRNA-binding protein; IGF = Insulin-like Growth Factor; mRNA = Messenger Ribonucleic Acid.) (section 7.2.1), two series of images have been acquired using fluorescence microscopy: one where the cell cytoplasm has been stained with GFP (Green Fluorescent Protein), the second where the nuclei have been stained with DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole). The first steps are detecting the nuclei on the DAPI images and learning a classification procedure into living cell or dead cell based on morphological and radiometric nuclei properties (average intensity, area, granularity, circularity...) (see Fig. 8).
|
A specific CellProfiler (http://cellprofiler.org) pipeline has been developed for this, and CellProfiler Analyst (http://cellprofiler.org/cp-analyst) has been used to learn a decision tree for automatic nuclei (hence, cell) classification. The next step is to segment (i.e., extract automatically the region of) the cell cytoplasms on the GFP images. Indeed, the target RNP-IMP granules appear in that compartment of the cell and are visible through their GFP response. We developed an active contour-based segmentation method relying on local image contrast with an initialization provided by a marked point process detection of ellipses [18] (see Fig. 8). Then, the detection of the particles can be performed inside the segmented cytoplasms (using a method called SPADE previously developed by the team).