Section: New Results
Matching problems and their applications
Participants : Laurent Baratchart, Martine Olivi, David Martinez Martinez, Fabien Seyfert.
This is collaborative work with Stéphane Bila (XLIM, Limoges, France), Yohann Sence (XLIM, Limoges, France), Thierry Monediere (XLIM, Limoges, France), Francois Torrès (XLIM, Limoges, France) in the context of the ANR Cocoram (see Section 7.2.1).
Filter synthesis is usually performed under the hypothesis that both ports of the filter are loaded on a constant resistive load (usually 50 Ohm). In complex systems, filters are however cascaded with other devices, and end up being loaded, at least at one port, on a non purely resistive frequency varying load. This is for example the case when synthesizing a multiplexer: each filter is here loaded at one of its ports on a common junction. Thus, the load varies with frequency by construction, and is not purely resistive either. Likewise, in an emitter-receiver, the antenna is followed by a filter. Whereas the antenna can usually be regarded as a resistive load at some frequencies, this is far from being true on the whole pass-band. A mismatch between the antenna and the filter, however, causes irremediable power losses, both in emission and transmission. Our goal is therefore to develop a method for filter synthesis that allows us to match varying loads on specific frequency bands, while enforcing some rejection properties away from the pass-band.
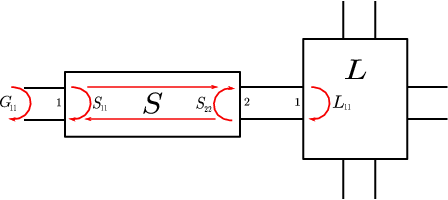
Figure 5 shows a filter with scattering matrix , plugged at its right port on a frequency varying load with reflection parameter . If the filter is lossless, simple algebraic manipulations show that on the frequency axis the reflex-ion parameter satisfies:
The matching problem of minimizing amounts therefore to minimize the pseudo-hyperbolic distance between the filter's reflex-ion parameter and the load's reflex-ion , on a given frequency band. On the contrary enforcing a rejection level on a stop band, amounts to maintaining the value of above a certain threshold on this frequency band. For a broad class of filters, namely those that can be modeled by a circuit of coupled resonators, the scattering matrix is a rational function of McMillan degree in the frequency variable. The matching problem thus appears to be a rational approximation problem in the hyperbolic metric.
Approach based on interpolation
When the degree of the rational function is fixed, the hyperbolic minimization problem is non-convex which leads us to seek methods to derive good initial guesses for classical descent algorithms. To this effect, if where , are polynomials, we considered the following interpolation problem : given frequency points and a transmission polynomial , to find a monic polynomial of degree such that:
where is the unique monic Hurwitz polynomial of degree satisfying the Feldtkeller equation
which accounts for the losslessness of the filter. The frequencies are perfect matching points where holds, while the real zeros of are perfect rejection points (i.e. ). The interpolation problem is therefore a point-wise version of our original matching-rejection problem. The monic restriction on and ensures the realizability of the filter in terms of coupled resonating circuits. If a perfect phase shifter is added in front of the filter, realized for example with a transmission line on a narrow frequency band, these monic restrictions can be dropped and an extra interpolation point is added, thereby yielding another interpolation problem . Our main result, states that as well as admit a unique solution. Moreover the evaluation map defined by is a homeomorphism from monic polynomials of degree onto ( the complex open disk), and is a diffeomorphism on an open, connected, dense set of . This last property has shown to be crucial for the design of an effective computational procedure based on continuation techniques. Current implementations of the latter tackle instances of or for in less than , and allow for a recursive use of this interpolation framework in multiplexer synthesis problems. We presented these techniques at the MTNS conference 2016 held in Mineapolis [17]. The detailed mathematical proofs can be found in [23] which is under review at SIMA, the SIAM journal on Mathematical Analysis.
Uniform matching and global optimality considerations
The previous interpolation procedure provides us with a matching/rejecting filtering characteristics at a discrete set of frequencies. This may serve as a starting point for heavier optimization procedures, where the matching and rejection specifications are expressed uniformly over the bandwidth. Although the practical results thus obtained have shown to be quite convincing, we have no proof of their global optimality. This led us to seek alternative approaches able to assess, at least in simple cases, global optimality of the derived response. By optimality we mean, as in classical filtering, the ability to derive the uniformly best matching response in a given pass-band, while ensuring some rejection constraints on a stop-band. Following the approach of Fano and Youla, we considered the problem of designing a loss-less frequency response, under the condition that a specified load can be "unchained" from one of its port. This classically amounts to set interpolation conditions on the response at the transmission zeros of the Darlington extension of the load. When the load admits a rational representation of degree 1, and if the transmission zeros of the overall system are fixed, then we were able to show that the uniform matching problem over an interval, together with rejection constraints at other frequency locations, reduces to a convex minimization problem with convex constraints over the set of non-negative polynomials of given degree. In this case, which is already of some practical interest for antenna matching (antennas usually exhibit a single resonance in their matching band which is decently approximated at order 1), it is therefore possible to perform filter synthesis with a guarantee on the global optimality of the obtained characteristics. The practical approach, relying on convex duality and linear programming is presented in [26], together with an implementation using a SIW (substrate integrated filter).