Section: New Results
Online Tracking Parameter Adaptation based on Evaluation
Participants : Duc Phu Chau, Julien Badie, Kartick Subramanian, François Brémond, Monique Thonnat.
Keywords: Object tracking, parameter tuning, online evaluation, machine learning
Several studies have been proposed for tracking mobile objects in videos [50] . For example we have proposed recently a new tracker which is based on co-inertia analysis (COIA) of object features [44] . However the parameter tuning is still a common issue for many trackers. In order to solve this problem, we propose an online parameter tuning process to adapt a tracking algorithm to various scene contexts. The proposed approach brings two contributions: (1) an online tracking evaluation, and (2) a method to adapt online tracking parameters to scene contexts.
In an offline training phase, this approach learns how to tune the tracker parameters to cope with different contexts. Different learning schemes (e.g. neural network-based) are proposed. A context database is created at the end of this phase to support the control process of the considered tracking algorithm. This database contains satisfactory parameter values of this tracker for various contexts.
In the online control phase, once the tracking quality is evaluated as not good enough, the proposed approach computes the current context and tunes the tracking parameters using the learned values.
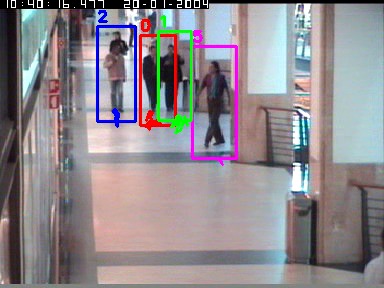
The experimental results show that the proposed approach improves the performance of the tracking algorithm and outperforms recent state of the art trackers. Figure 23 shows the correct tracking results of four people while occlusions happen. Table 3 presents the tracking results of the proposed approach and of some recent trackers from the state of the art. The proposed controller increases significantly the performance of an appearance-based tracker [63] . We obtain the best value (i.e. mostly tracked trajectories) compared to state of the art trackers.
|
| Approaches | MT (%) | PT (%) | ML (%) |
| Xing et al. [92] | 84.3 | 12.1 | 3.6 |
| Li et al. [76] | 84.6 | 14.0 | 1.4 |
| Kuo et al. [74] | 84.6 | 14.7 | 0.7 |
| D.P Chau et al. [63] without the proposed approach | 78.3 | 16.0 | 5.7 |
| D.P Chau et al. [63] with the proposed approach | 85.5 | 9.2 | 5.3 |