Section: New Results
3D Coronary vessel tracking in x-ray projections
Participants : Emmanuelle Poulain, Grégoire Malandain.
This work is made in collaboration with Régis Vaillant (GE-Healthcare, Buc, France) and Nicholas Ayache (Inria Epione team).
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) is a minimally procedure which is used to treat coronary artery narrowing. The physician intervenes on the patient under the guidance of an x-ray imaging system. This system is not able to display a visual assessment of the coronary wall, contrary to the pre-operative Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA). To help physician to exploit this information during the course of the procedure, registering these two modalities would be useful. To this aim, we first proposed in a previous work a method of 3D coronary tracking of the main vessel in x-ray projections [17]. Although, we faced a segmentation problem when we wanted to move from the tracking of one vessel to the entire set. For this reason, we have worked this year on the vessel centerline extraction in x-ray projection images.
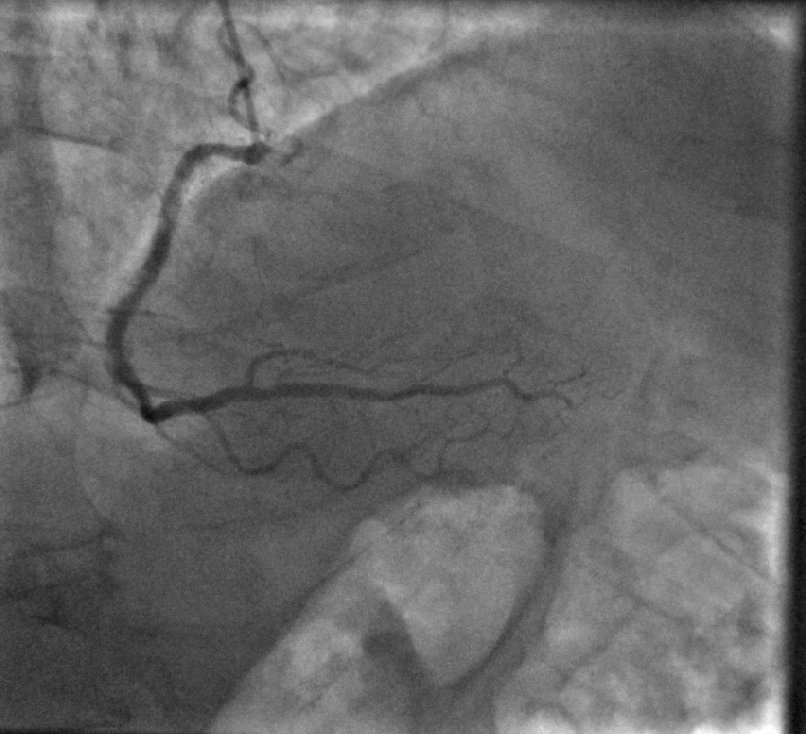
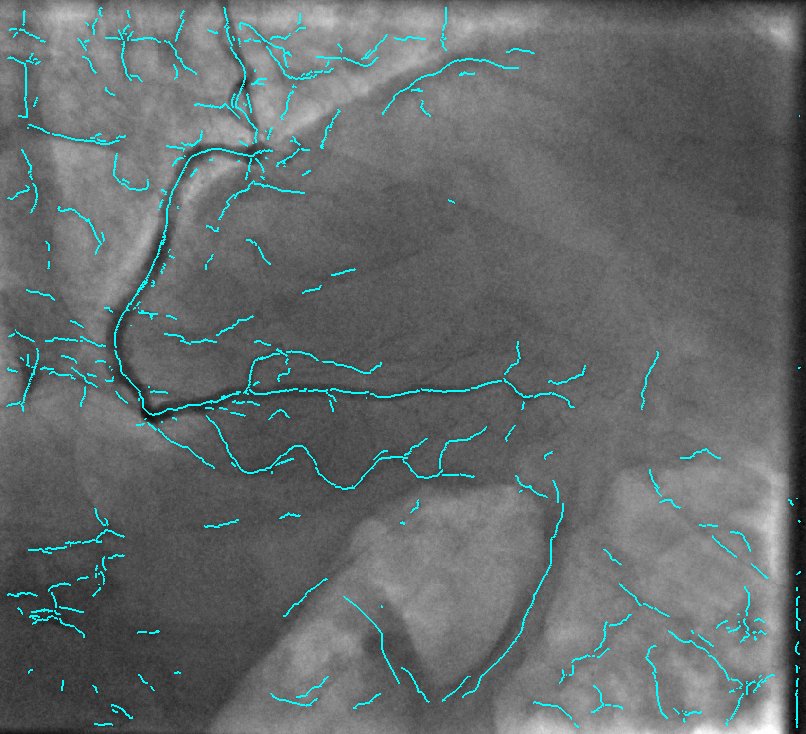
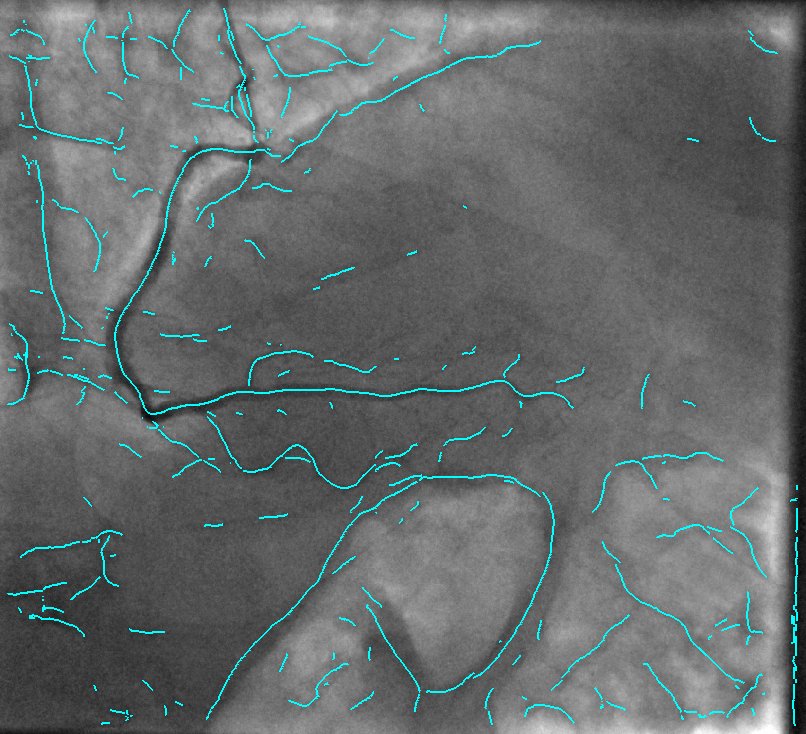
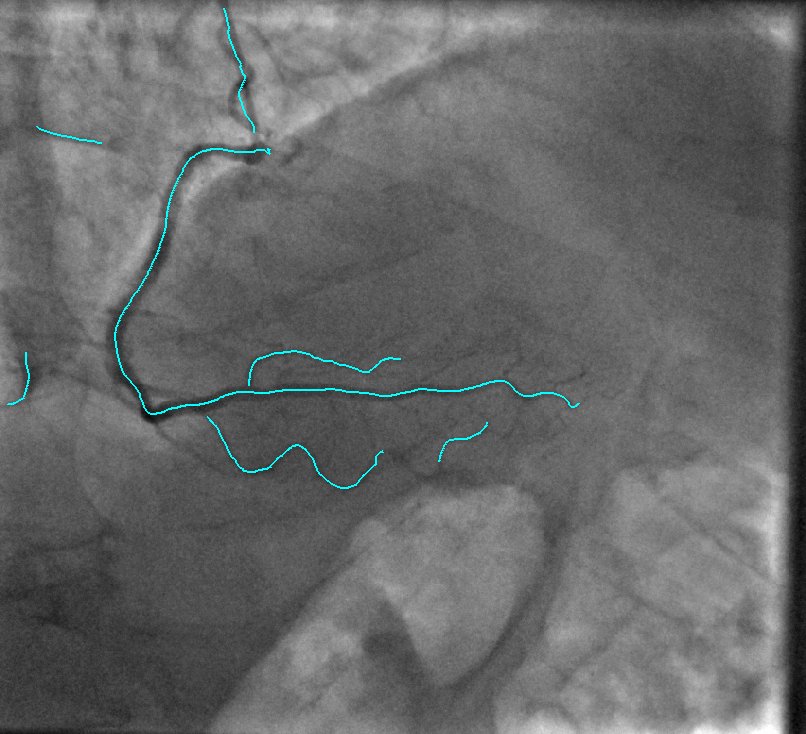
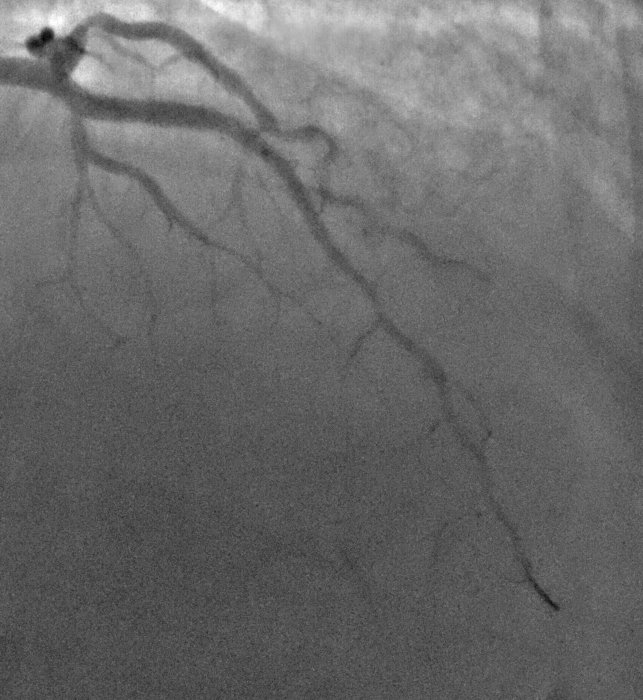
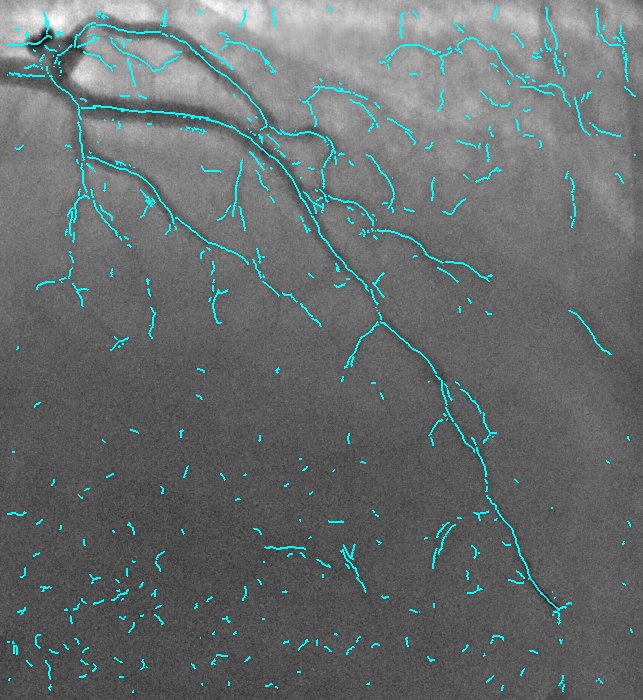
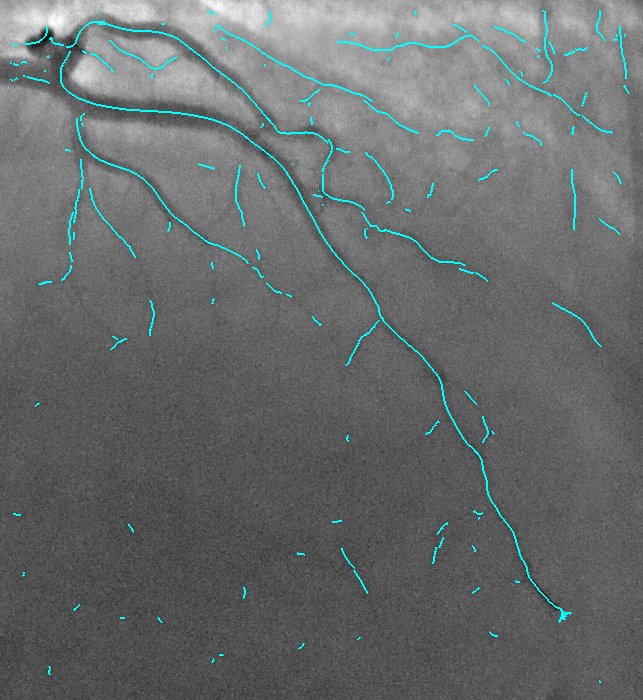
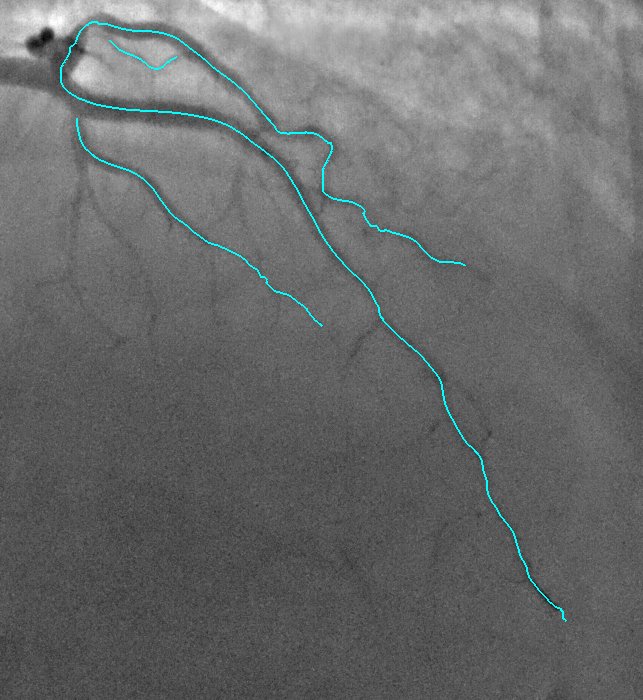
2D Angiographic images are often first enhanced, before centerline extraction, by dedicated filters, e.g. Hessian based filters. Such filters exhibit critical defects, one of them being the non-uniform response for vessels of different sizes. This fact largely compromised the next step of centerline extraction. This last step requires a threshold step which is usually not clearly explained in other established methods. We worked on a model-based study of two widely used Hessian-based filter. It demonstrates that the non-uniform response for vessels of different sizes is due to the projective effect, and further enables to propose an X-ray projection dedicated method for centerline extraction which overpass this behavior. It is complemented by a component-based hysteresis thresholding. Last, the huge variability of coronary image aspect, due to imaging parameters, makes the threshold choice quite complex. We have shown that the thresholds can be determined automatically taking into account the kilovoltage peak (kVp), one key technical parameter of the X-ray acquisition. These thresholds are determined without any a priori on the image content. This technique not only allows to obtain an almost optimal segmentation, but also performs well for non-injected frames. Results of our proposed method and methods from state of the art are presented in Fig. 9.
|