Section: New Results
Correlation-based method for membrane diffusion estimation during exocytosis in TIRFM
Participants : Ancageorgiana Caranfil, Charles Kervrann.
The dynamics of the plasma membrane of the cell is not fully understood yet; one of the crucial aspects to clarify is the diffusion process during exocytosis. Several image acquisition modalities exist, including TIRFM (Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence Microscopy), that have successfully been used to determine the successive steps of exocytosis. However, computing characteristic values for plasma membrane dynamics is problematic, as the experimental conditions have a strong influence on the obtained data, and a general model of molecular interaction dynamics cannot be determined.
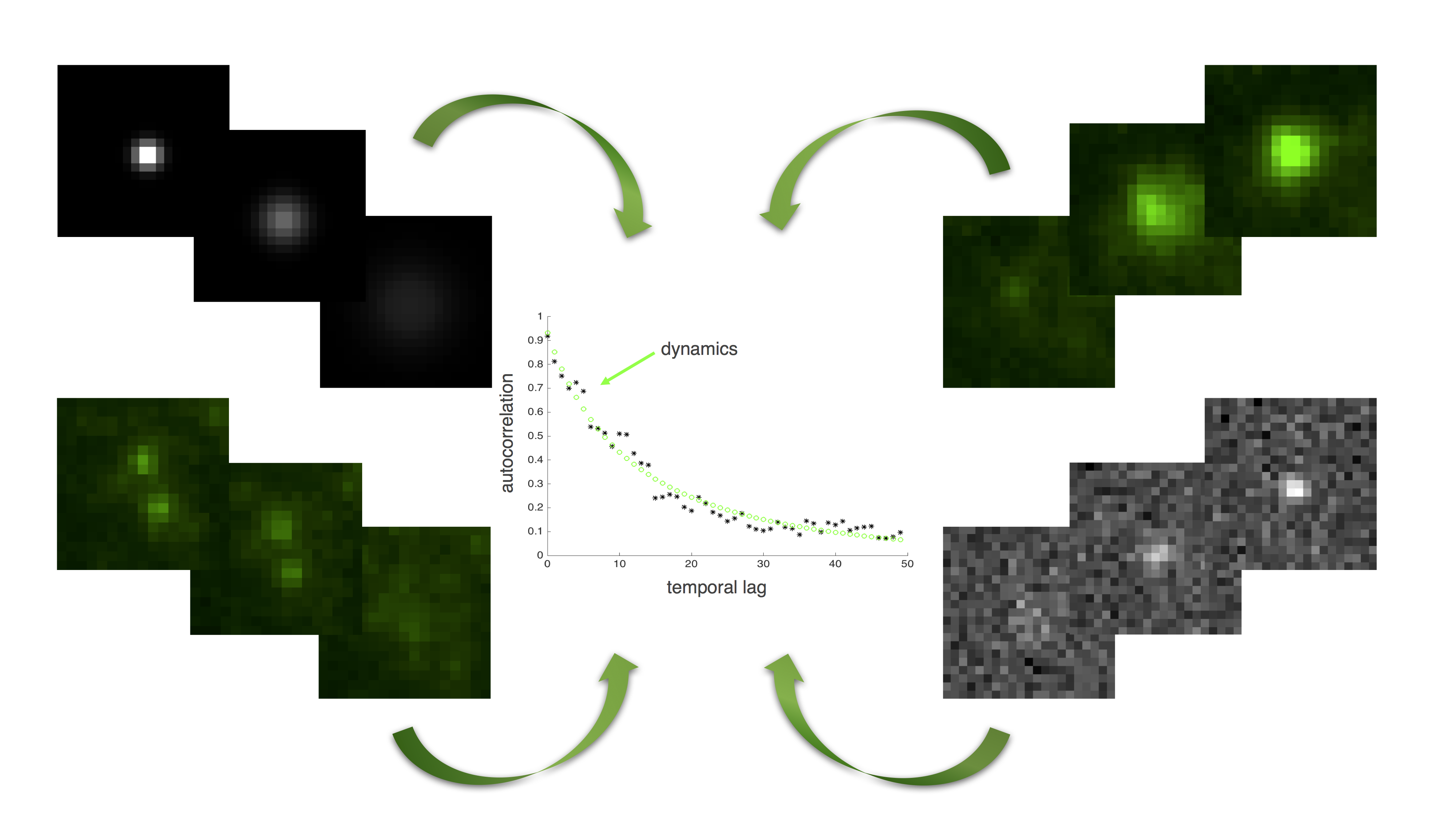
This year, we have continued our study of correlation-based methods for local diffusion estimation in TIRFM images. Our original method was tested on both synthetic and real images showing an isolated diffusion event, and a robust algorithm was developed to cope with noisy data. Our first model was linear and had only two parameters to estimate. Diffusion coefficient estimation was accurate on synthetic images even with moderate to low signal-to-noise ratio, and within reasonable margins of error on real images with little noise. We have then extended our mathematical model by using a global approach subject to initial local diffusion conditions. Isolated diffusion events are well described, but this new model can also handle the case of noisy images with non-uniform background, and the case of two or more diffusion events in the region of interest. The extended model is non-linear but has few parameters to estimate. An iterative minimization method is used to fit the model parameters to the data points (see Fig. 5). Despite non-linearity, results are accurate on images with pure diffusion events and show robustness to background. The quality of parameters estimation is barely influenced by the length and size of the input TIRFM sequence, which is not the case with standard correlation methods. We have thus developed a correlation-based method that is able to estimate diffusion in a variety of cases in TIRFM images (Fig. 5).
Collaborators: Francois Waharte (UMR 144 CNRS-Institut Curie, PICT-IBiSA),
Perrine Paul-Gilloteaux (UMS 3556, IRS-UN, Nantes).
|